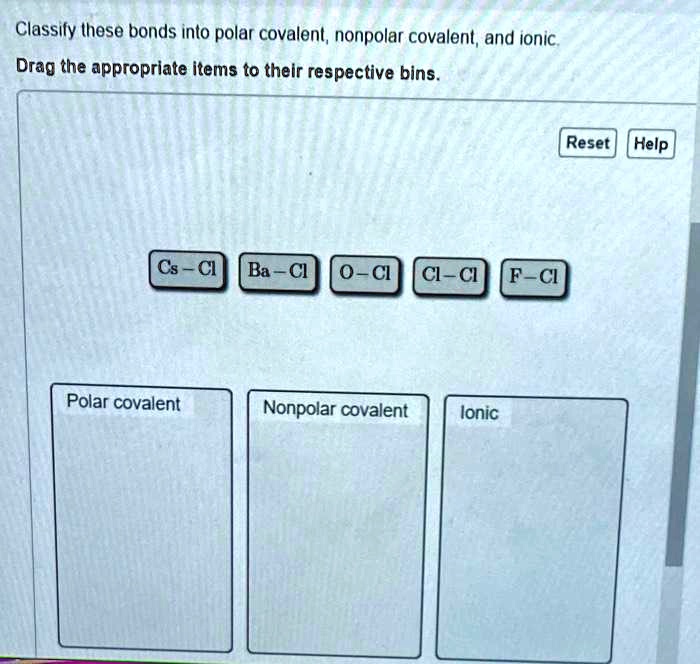
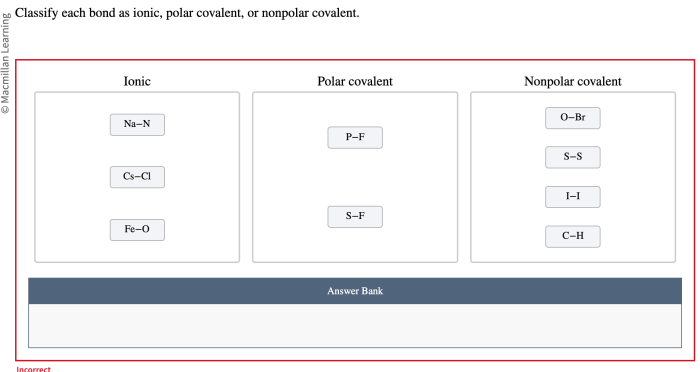
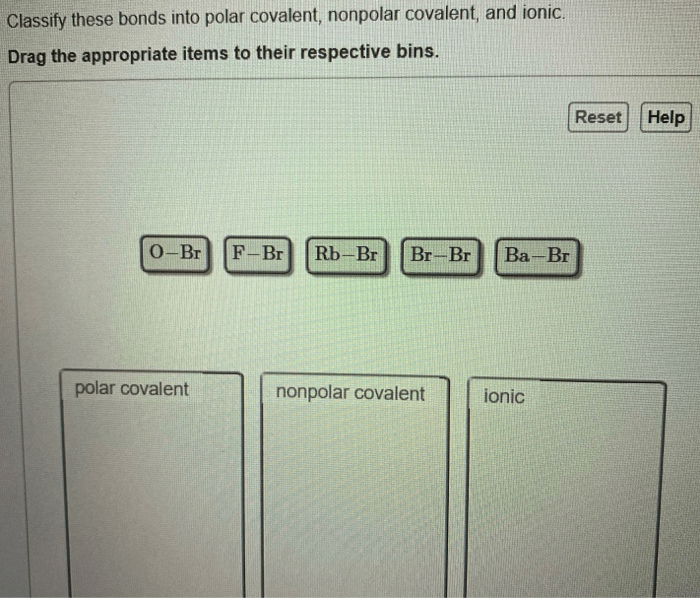
Classify these bonds as ionic polar covalent or nonpolar covalent takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Understanding the nature of chemical bonds is crucial for comprehending the behavior of atoms and molecules. Bonds can be classified into three main types: ionic, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent. This classification is based on the electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms and provides valuable insights into their properties and reactivity.
Understanding Bond Types
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together to form molecules. There are three main types of chemical bonds: ionic, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent. These bonds differ in their strength, polarity, and the way they are formed.
Ionic bonds are formed between atoms of metals and nonmetals. In an ionic bond, one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom. The atom that loses electrons becomes a positively charged ion, while the atom that gains electrons becomes a negatively charged ion.
The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, forming an ionic bond.
Polar covalent bonds are formed between atoms of different electronegativities. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons. In a polar covalent bond, the more electronegative atom attracts the electrons in the bond more strongly than the less electronegative atom.
This creates a partial positive charge on the less electronegative atom and a partial negative charge on the more electronegative atom. The partial charges create a dipole moment, which is a measure of the polarity of the bond.
Nonpolar covalent bonds are formed between atoms of the same electronegativity. In a nonpolar covalent bond, the electrons are shared equally between the two atoms. This creates no partial charges and no dipole moment.
Classifying Bonds, Classify these bonds as ionic polar covalent or nonpolar covalent
The type of bond formed between two atoms can be classified based on the difference in electronegativity between the atoms. The following table summarizes the criteria for classifying bonds as ionic, polar covalent, or nonpolar covalent:
| Bond Type | Difference in Electronegativity |
|---|---|
| Ionic | > 1.7 |
| Polar Covalent | 0.5
|
| Nonpolar Covalent | < 0.5 |
Factors Influencing Bond Type
The type of bond formed between two atoms is influenced by several factors, including electronegativity, atomic size, and molecular geometry.
Electronegativity is the most important factor in determining the type of bond formed. The greater the difference in electronegativity between two atoms, the more polar the bond will be. If the difference in electronegativity is large enough, the bond will be ionic.
Atomic size also plays a role in determining the type of bond formed. The larger the atoms, the less polar the bond will be. This is because the electrons in larger atoms are more spread out, which makes them less likely to be attracted to the nucleus of the other atom.
Molecular geometry also affects the type of bond formed. For example, in a linear molecule, the electrons are more likely to be shared equally between the atoms, resulting in a nonpolar covalent bond. In a bent molecule, the electrons are more likely to be concentrated on one atom, resulting in a polar covalent bond.
Properties of Different Bond Types
Ionic, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent bonds have different properties. Ionic bonds are typically strong and brittle. Polar covalent bonds are typically weaker than ionic bonds, but they are more flexible. Nonpolar covalent bonds are typically the weakest type of bond.
Ionic bonds are polar, meaning they have a positive end and a negative end. Polar covalent bonds are also polar, but they have a smaller dipole moment than ionic bonds. Nonpolar covalent bonds are nonpolar, meaning they have no dipole moment.
Ionic bonds are soluble in water, while polar covalent bonds are partially soluble in water. Nonpolar covalent bonds are insoluble in water.
Applications of Bond Classification
Bond classification is an important tool for understanding chemical reactions. By understanding the type of bond between two atoms, chemists can predict how the atoms will react with each other.
For example, ionic bonds are typically formed between metals and nonmetals. This means that metals are likely to react with nonmetals to form ionic compounds. Polar covalent bonds are typically formed between atoms of different electronegativities. This means that atoms of different electronegativities are likely to react with each other to form polar covalent compounds.
Bond classification can also be used to predict the properties of molecules. For example, molecules with ionic bonds are typically strong and brittle. Molecules with polar covalent bonds are typically weaker and more flexible. Molecules with nonpolar covalent bonds are typically the weakest and most flexible.
Popular Questions: Classify These Bonds As Ionic Polar Covalent Or Nonpolar Covalent
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds involve the complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of charged ions. Covalent bonds, on the other hand, involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
How do you determine the polarity of a covalent bond?
The polarity of a covalent bond is determined by the electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms. A higher electronegativity difference results in a more polar bond.
What factors influence the strength of a chemical bond?
The strength of a chemical bond is influenced by factors such as bond length, bond order, and the electronegativity of the bonded atoms.