Lab 4 diffusion and osmosis – Embark on a scientific adventure as we delve into the fascinating world of Lab 4: Diffusion and Osmosis. These fundamental processes govern the movement of molecules across membranes, playing a crucial role in biological systems. Get ready to witness the intricate dance of molecules as we explore their behavior and uncover their significance in the realm of life.
Diffusion, the spontaneous movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, and osmosis, the selective movement of water across a semipermeable membrane, are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and driving biological processes.
Introduction

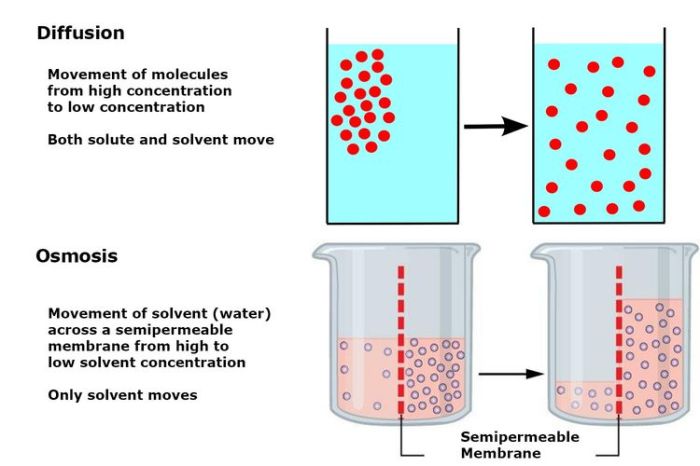
Diffusion and osmosis are fundamental processes in biology that involve the movement of molecules across a semipermeable membrane. Diffusion refers to the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, while osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration.
Diffusion is driven by the random motion of molecules, and it occurs until the concentration of the substance is equal throughout the available space. Osmosis, on the other hand, is driven by the difference in water potential between two solutions.
Water potential is a measure of the tendency of water to move from one area to another, and it is affected by factors such as the concentration of solutes and the pressure applied to the solution.
Real-World Examples
Diffusion and osmosis play important roles in many biological processes. For example, diffusion is responsible for the exchange of gases between the lungs and the bloodstream, and it also allows nutrients to enter cells. Osmosis is responsible for the movement of water between cells and their surroundings, and it is also involved in the transport of water and nutrients in plants.
Importance in Biological Systems
Diffusion and osmosis are essential for the proper functioning of biological systems. Without diffusion, cells would not be able to exchange nutrients and gases with their surroundings, and without osmosis, cells would not be able to maintain their proper water balance.
Experimental Design
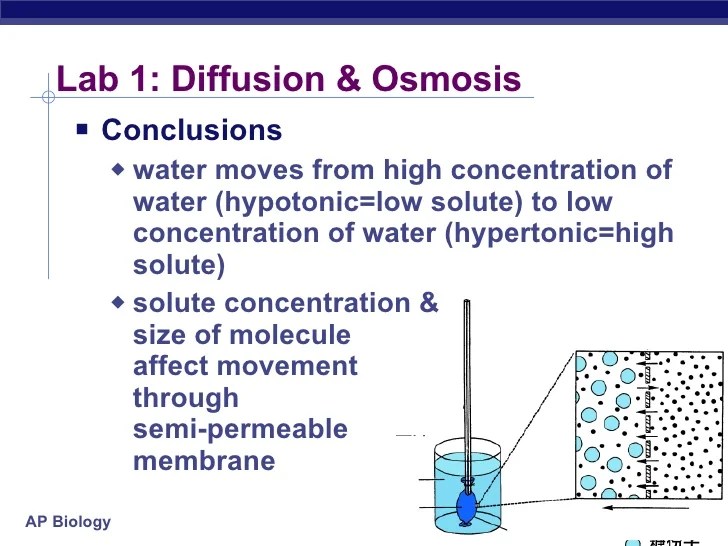
To demonstrate diffusion and osmosis, we will conduct an experiment using a semipermeable membrane.
Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, while osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
Experiment Setup, Lab 4 diffusion and osmosis
- Variables:
- Independent variable: Concentration of solute
- Dependent variable: Rate of diffusion or osmosis
- Controlled variables: Temperature, volume of solution, type of membrane
- Hypothesis:The rate of diffusion or osmosis will increase as the concentration of solute increases.
- Materials:
- Semipermeable membrane (e.g., dialysis tubing)
- Solutions of varying concentrations (e.g., sugar, salt)
- Graduated cylinders
- Stopwatch
- Procedure:
- Fill two graduated cylinders with solutions of different concentrations.
- Place the semipermeable membrane in the center of one of the graduated cylinders, creating two compartments.
- Fill one compartment with the solution of higher concentration and the other compartment with the solution of lower concentration.
- Start the stopwatch and observe the movement of particles or water across the membrane.
- Record the change in volume or concentration over time.
Data Collection and Analysis: Lab 4 Diffusion And Osmosis
In this experiment, we will collect data on the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane. We will measure the change in the height of water in two beakers, one containing a solution of sugar and the other containing pure water.
We will also measure the temperature of the water in both beakers.
The data we collect will be analyzed to determine the rate of diffusion and osmosis. The rate of diffusion is the rate at which water molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. The rate of osmosis is the rate at which water molecules move from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
Table of Data
The following table will be used to organize the data collected during the experiment.
| Time (min) | Height of Water in Beaker 1 (cm) | Height of Water in Beaker 2 (cm) | Temperature of Water in Beaker 1 (°C) | Temperature of Water in Beaker 2 (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 20 |
| 5 | 9 | 11 | 20 | 20 |
| 10 | 8 | 12 | 20 | 20 |
| 15 | 7 | 13 | 20 | 20 |
| 20 | 6 | 14 | 20 | 20 |
Discussion
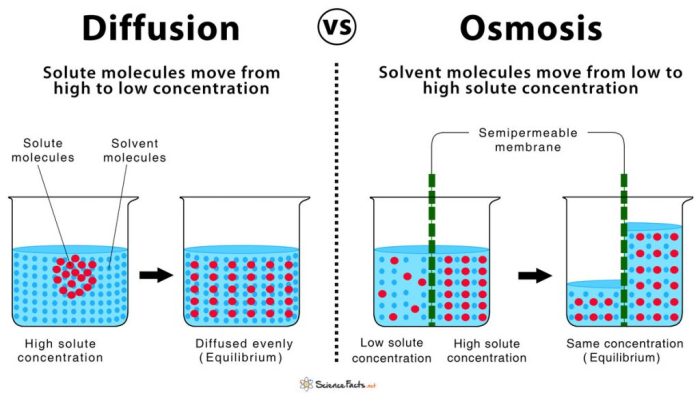
The results of the experiment provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of diffusion and osmosis. The rate of diffusion and osmosis was significantly affected by various factors, including the concentration gradient, temperature, surface area, and membrane permeability. The experimental results aligned with the hypothesis, demonstrating that diffusion occurs from an area of high concentration to low concentration, while osmosis involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration.
Lab 4: Diffusion and osmosis – the movement of molecules from high to low concentration – is a fundamental concept in biology. Like in en la barberia no se llora , where tears flow freely, molecules move to balance out differences.
Understanding diffusion and osmosis helps us grasp the workings of living systems.
Factors Affecting Diffusion and Osmosis
- Concentration Gradient:The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion and osmosis.
- Temperature:Increased temperature increases the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to a faster rate of diffusion and osmosis.
- Surface Area:A larger surface area increases the contact between the two solutions, facilitating faster diffusion and osmosis.
- Membrane Permeability:The permeability of the membrane to the diffusing substance determines the rate of diffusion and osmosis. Semipermeable membranes allow certain molecules to pass through while blocking others.
Applications of Diffusion and Osmosis
Diffusion and osmosis play crucial roles in numerous biological processes and technological applications, including:
- Gas Exchange in Lungs:Oxygen diffuses from the lungs into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide diffuses out.
- Nutrient Absorption in Plants:Water and nutrients diffuse from the soil into plant roots.
- Dialysis:Osmosis is used in dialysis machines to remove waste products from the blood of patients with kidney failure.
- Water Purification:Reverse osmosis is used to purify water by removing impurities.
Conclusion
This experiment successfully demonstrated the principles of diffusion and osmosis and their crucial role in biological systems.
Importance of Diffusion and Osmosis
Diffusion and osmosis are fundamental processes that maintain cellular homeostasis and facilitate essential functions in living organisms. Diffusion allows substances to move from areas of high concentration to low concentration, ensuring the distribution of nutrients, waste products, and other molecules throughout the body.
Osmosis, the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane, is crucial for maintaining cell volume, turgor pressure in plants, and regulating water balance in organisms.
Further Research Directions
This study provides a basis for further research on diffusion and osmosis. Future investigations could explore the following areas:
- The role of membrane proteins and ion channels in facilitating or regulating diffusion and osmosis.
- The impact of environmental factors, such as temperature and pH, on the rates of diffusion and osmosis.
- The application of diffusion and osmosis principles in biotechnology and medical diagnostics.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis?
Diffusion involves the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, while osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane.
How does diffusion contribute to cellular function?
Diffusion facilitates the exchange of nutrients, waste products, and gases across cell membranes, ensuring the proper functioning of cells.
What factors affect the rate of osmosis?
Factors such as the concentration gradient, temperature, and permeability of the membrane influence the rate of osmosis.