Which is the compressed format of the ipv6 address – In the realm of computer networking, IPv6 address compression plays a pivotal role in optimizing network efficiency and performance. This technique, which reduces the length of IPv6 addresses, offers significant advantages in network configurations and data transmission. This article delves into the intricacies of IPv6 address compression, exploring its types, techniques, and practical applications.
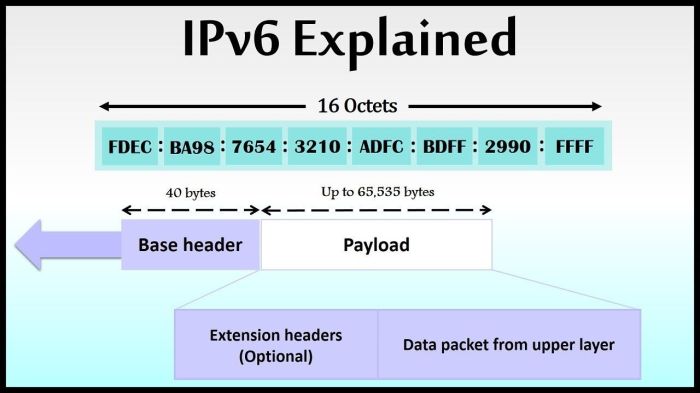
IPv6 addresses, represented as a sequence of eight hexadecimal numbers separated by colons, can be cumbersome and difficult to manage. Address compression techniques address this challenge by reducing the number of characters required to represent an IPv6 address, making it more compact and easier to handle.
IPv6 Address Compression
IPv6 address compression is a technique used to shorten the representation of IPv6 addresses by removing unnecessary zeros and using hexadecimal notation. It simplifies the readability, reduces the size of network packets, and enhances network efficiency.
There are several types of IPv6 address compression techniques, including double colon notation and zero suppression.
Double Colon Notation
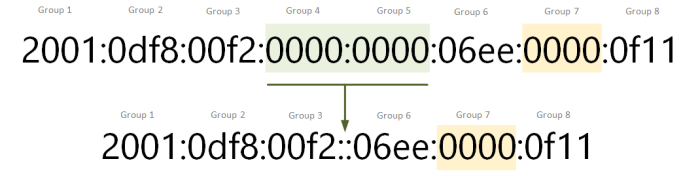
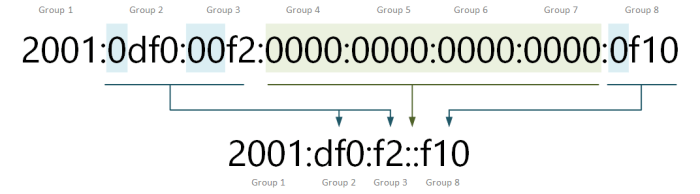
Double colon notation uses two consecutive colons (::) to represent a series of consecutive zero segments in an IPv6 address. For example, the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:0000:1428:57ab can be compressed using double colon notation as 2001:0db8::1428:57ab.
Advantages of using double colon notation include:
- Simplicity and readability
- Reduced size of network packets
Limitations include:
- Ambiguity in cases where multiple consecutive zero segments exist
Zero Suppression
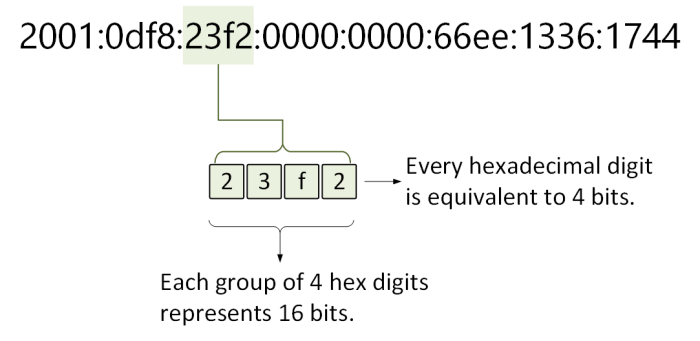
Zero suppression involves removing leading zeros from each hexadecimal segment of an IPv6 address. For example, the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:0000:1428:57ab can be compressed using zero suppression as 2001:db8::1428:57ab.
Advantages of using zero suppression include:
- Reduced size of network packets
- Improved readability compared to uncompressed addresses
Limitations include:
- Potential for ambiguity in cases where multiple leading zeros exist
Combining Techniques, Which is the compressed format of the ipv6 address
Double colon notation and zero suppression can be combined to further compress IPv6 addresses. For example, the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:0000:1428:57ab can be compressed using both techniques as 2001:db8::1428:57ab.
Combining compression techniques offers the benefits of both methods, resulting in shorter and more readable addresses.
Practical Applications
IPv6 address compression is widely used in network configurations to improve efficiency and performance. It reduces the size of routing tables and network packets, leading to faster transmission and reduced bandwidth consumption.
Limitations and challenges of using IPv6 address compression include:
- Potential for ambiguity in cases where multiple compression techniques are applied
- Compatibility issues with older network devices that do not support IPv6 address compression
User Queries: Which Is The Compressed Format Of The Ipv6 Address
What is the purpose of IPv6 address compression?
IPv6 address compression aims to reduce the length of IPv6 addresses, making them more compact and easier to manage. It simplifies network configurations, improves data transmission efficiency, and enhances security.
How does double colon notation work in IPv6 address compression?
Double colon notation allows the omission of consecutive zero segments in an IPv6 address. It uses two colons (::) to represent the longest sequence of consecutive zero segments, reducing the address length.
What are the limitations of using IPv6 address compression?
IPv6 address compression may not be suitable in all scenarios. For instance, it can introduce ambiguity when multiple zero segments exist in an address. Additionally, some legacy systems and applications may not support compressed IPv6 addresses.