Riparian rights vs littoral rights – Riparian rights vs. littoral rights: a legal landscape that governs the complex relationship between water bodies and the properties that border them. From the shores of rivers to the edges of oceans, these rights shape the way we interact with and protect our precious aquatic resources.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the definitions, similarities, and differences between riparian and littoral rights, examining their acquisition, exercise, and the legal limitations that govern their use. We uncover the importance of these rights for water management, environmental conservation, and the delicate balance between human activity and the natural world.
Riparian Rights

Riparian rights are legal rights that attach to land that borders a river, stream, or other body of water. These rights allow the landowner to use the water for various purposes, such as drinking, irrigation, and recreation. Riparian rights are based on the common law principle that landowners have a right to the reasonable use of the water that flows past their property.
The legal basis for riparian rights can be traced back to ancient Roman law. In the Roman Empire, landowners were granted the right to use the water that flowed past their property for domestic purposes, such as drinking, bathing, and watering livestock.
This right was later extended to include the use of water for irrigation and other agricultural purposes.
In the United States, riparian rights are governed by state law. Each state has its own set of rules and regulations that determine the scope and extent of riparian rights. In general, riparian rights are limited to the reasonable use of the water.
This means that landowners cannot use the water in a way that harms other landowners or that damages the environment.
There are a number of different ways to acquire riparian rights. The most common way is to own land that borders a body of water. Riparian rights can also be acquired through prescription, which is a legal doctrine that allows a person to acquire rights to property by using it openly and notoriously for a long period of time.
Riparian rights are important because they allow landowners to use the water that flows past their property for a variety of purposes. These rights are essential for agriculture, industry, and recreation. Riparian rights also play an important role in protecting the environment.
By limiting the amount of water that landowners can use, riparian rights help to ensure that there is enough water for all users.
Littoral Rights

Littoral rights are legal rights that attach to land that borders a sea, ocean, or other large body of water. These rights allow the landowner to use the water for various purposes, such as fishing, boating, and swimming. Littoral rights are based on the common law principle that landowners have a right to the reasonable use of the water that borders their property.
The legal basis for littoral rights can be traced back to ancient Roman law. In the Roman Empire, landowners were granted the right to use the water that bordered their property for domestic purposes, such as drinking, bathing, and watering livestock.
This right was later extended to include the use of water for fishing, boating, and other recreational purposes.
In the United States, littoral rights are governed by state law. Each state has its own set of rules and regulations that determine the scope and extent of littoral rights. In general, littoral rights are limited to the reasonable use of the water.
This means that landowners cannot use the water in a way that harms other landowners or that damages the environment.
There are a number of different ways to acquire littoral rights. The most common way is to own land that borders a body of water. Littoral rights can also be acquired through prescription, which is a legal doctrine that allows a person to acquire rights to property by using it openly and notoriously for a long period of time.
Littoral rights are important because they allow landowners to use the water that borders their property for a variety of purposes. These rights are essential for fishing, boating, swimming, and other recreational activities. Littoral rights also play an important role in protecting the environment.
By limiting the amount of water that landowners can use, littoral rights help to ensure that there is enough water for all users.
Similarities and Differences Between Riparian and Littoral Rights: Riparian Rights Vs Littoral Rights
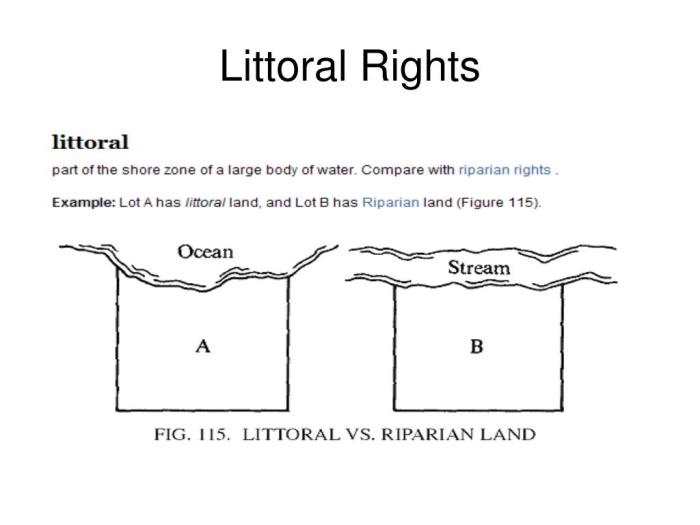
Riparian rights and littoral rights are both legal rights that attach to land that borders a body of water. However, there are some key similarities and differences between the two types of rights.
- Similarities:
- Both riparian rights and littoral rights are based on the common law principle that landowners have a right to the reasonable use of the water that borders their property.
- Both riparian rights and littoral rights can be acquired through ownership of land that borders a body of water or through prescription.
- Both riparian rights and littoral rights are limited to the reasonable use of the water. This means that landowners cannot use the water in a way that harms other landowners or that damages the environment.
- Differences:
- Riparian rights attach to land that borders a river, stream, or other freshwater body. Littoral rights attach to land that borders a sea, ocean, or other saltwater body.
- Riparian rights are typically more limited in scope than littoral rights. This is because rivers and streams are typically smaller and more vulnerable to damage than seas and oceans.
- Littoral rights include the right to use the water for fishing, boating, and other recreational purposes. Riparian rights do not typically include these rights.
| Characteristic | Riparian Rights | Littoral Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Type of water body | Freshwater | Saltwater |
| Scope of rights | More limited | More extensive |
| Recreational rights | Typically not included | Included |
FAQ Corner
What is the primary difference between riparian and littoral rights?
Riparian rights are associated with freshwater bodies such as rivers and streams, while littoral rights apply to saltwater bodies such as oceans and lakes.
How are riparian and littoral rights acquired?
These rights are typically acquired through ownership of land that borders a water body.
What are the common limitations on riparian and littoral rights?
These rights are subject to government regulations, environmental laws, and the reasonable use doctrine, which prevents individuals from unreasonably interfering with the rights of others.
